DOE Awards $504 Million Loan Guarantee to Utah Hydrogen Storage Project
(P&GJ) — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) closed on a $504.4 million loan guarantee to Mitsubishi Power Americas and Magnum Development to help finance the construction of the Advanced Clean Energy Storage I project in Utah, the world’s largest industrial green hydrogen storage facility.
The loan guarantee is the first for a new clean energy technology project from DOE’s Loan Programs Office (LPO) since 2014.
“Since President Biden’s first day in office, DOE has made it a priority to leverage the potential of the Loan Programs Office to fund emerging technologies that will deploy clean and reliable energy to Americans,” U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer M. Granholm said. “Accelerating the commercial deployment of clean hydrogen as a zero-emission, long-term energy storage solution is the first step in harnessing its potential to decarbonize our economy, create good paying clean energy jobs and enable more renewables to be added to the grid.”
The project is expected to create up to 400 jobs, adding a projected 25 full-time operations and maintenance personnel. It is set to help advance President Biden’s goal of net zero emissions by 2050 through clean energy deployment, as well as replacing a retiring coal-fired power plant.
“The Advanced Clean Energy Storage team, with its world-class industry partners, is excited to secure this loan by DOE to develop the first phase of the world’s largest renewable hydrogen energy hub,” said Michael Ducker, senior vice president of Hydrogen Infrastructure for Mitsubishi Power Americas and president of Advanced Clean Energy Storage I. “This step creates a path to accelerate the long-term hydrogen market and clean energy landscape to expand decarbonization across the United States.”
The Advanced Clean Energy Storage hub will help the clean energy transition by supporting the Intermountain Power Agency’s IPP Renewed Project—upgrading to an 840-megawatt (MW) hydrogen-capable gas turbine combined cycle power plant. The plant will initially run on a blend of 30% green hydrogen and 70% natural gas starting in 2025 and incrementally expand to 100% green hydrogen by 2045.
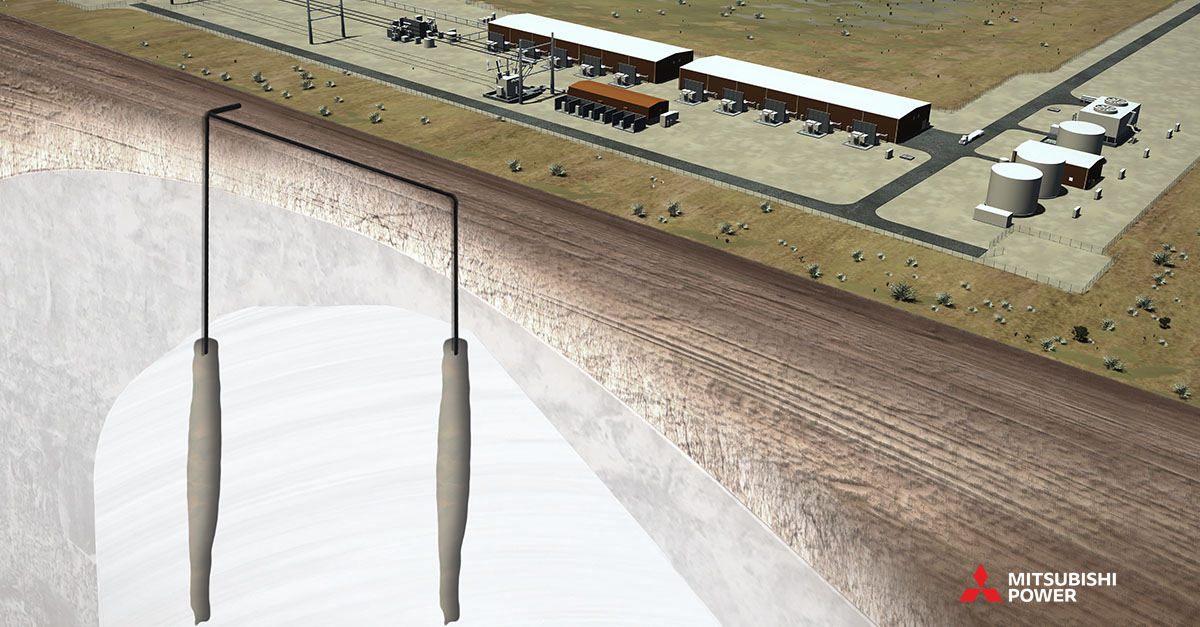
The hub will produce up to 100 metric tonnes per day of green hydrogen from renewable energy using electrolysis. Green hydrogen can then be stored in two massive salt caverns, each capable of storing 150 gigawatt hours (GWh) of energy, resulting in the world’s single largest hydrogen storage site, and providing capabilities for seasonal shifting of excess renewable energy.
The long-duration energy storage capability of the salt caverns will help improve resource adequacy and decrease costs by capturing excess renewable power when it is abundant and dispatching it back on the grid when it is needed.
In May, the LPO reviewed 77 applications for projects in 24 states, totaling nearly $79 billion in requested loans and loan guarantees, according to the DOE.
Related News
Related News

- Keystone Oil Pipeline Resumes Operations After Temporary Shutdown
- Freeport LNG Plant Runs Near Zero Consumption for Fifth Day
- Biden Administration Buys Oil for Emergency Reserve Above Target Price
- Mexico Seizes Air Liquide's Hydrogen Plant at Pemex Refinery
- Enbridge to Invest $500 Million in Pipeline Assets, Including Expansion of 850-Mile Gray Oak Pipeline
- Enbridge Receives Approval to Begin Service on Louisiana Venice Gas Pipeline Project
- U.S. to Acquire 3 Million Barrels of Oil for Emergency Reserve in September
- AG&P LNG Acquires 49% Stake in Vietnam's Cai Mep LNG Terminal
- BP's Carbon Emissions Increase in 2023, Ending Decline Since 2019
- Texas Sues EPA Over Methane Emission Rules for Oil and Gas Sector




Comments