September 2019, Vol. 246, No. 9
Features
Natural Gas-Burning Power Plant Operations Vary During Cold Weather
By Energy Information Administration (EIA)
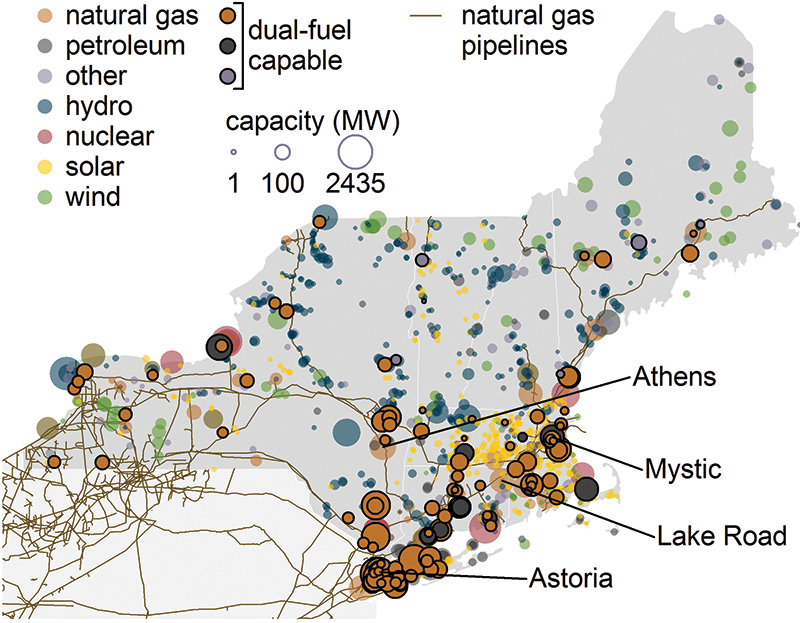
Power generation in New England and New York is largely dependent on natural gas, which accounts for more than half of the region’s electricity generating capacity.
About 58% of New England’s natural gas capacity has dual-fuel capability, meaning it can switch to other fuels such as petroleum-based fuels. Data from the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) continuous emissions monitoring system (CEMS) reveals how certain plants in New England and New York switch between fuels in certain situations.
Weather can have a significant effect on both electricity and natural gas demand. During times when natural gas supply is constrained, particularly during the winter, some plants are forced to reduce their output, or shut down entirely, as individual fuel sources become unavailable.
Plants with duel-fuel capability, however, are able to switch to a different fuel. The dual-fuel capability of natural gas-fired generators in the New England and New York regions has proven critically important for maintaining grid reliability, particularly during cold weather events that create increased demand for both natural gas and electricity.
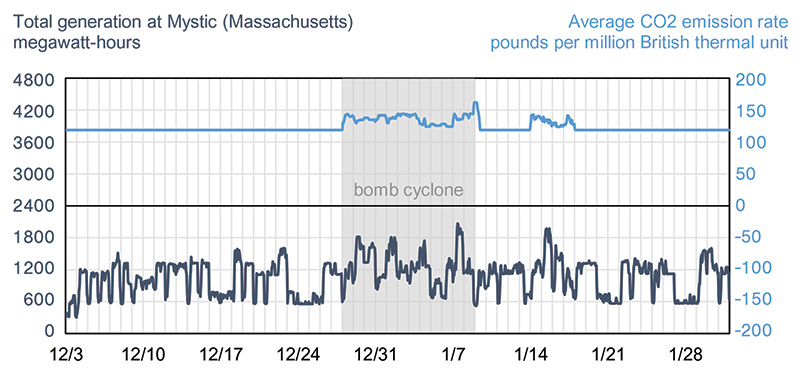
The bomb cyclone event, which spanned from Dec. 28, 2017, to Jan. 8, 2018, highlighted the value of dual-fuel capability when unusually cold weather created additional demand for natural gas for heating which, in turn, reduced the availability of the fuel for electricity generation.
During this event, several dual-fuel capable generators switched from natural gas to petroleum to continue generating electricity.
EPA gathers hourly power plant operations and CEMS data through the Air Markets Program from most of the fossil fuel generating capacity in the United States. In the New England and New York regions, CEMS data are collected for 33 gigawatts (GW) of the 36 GW of natural gas capacity.
CEMS measures both CO2 emissions and the consumed energy input for each power plant. The relative values of CO2 emissions and energy inputs can be used to determine the energy source burned.
For example, the combustion of natural gas produces 117 pounds of CO2 per million British thermal units (MMBtu), and petroleum, which has a higher carbon content, produces 161 pounds of CO2 MMBtu.
Reviewing a plant’s operating profile over time can reveal how it reacts to events that affect electric reliability. The following examples show how different types of plants reacted during the cold weather event of late December 2017 and early January 2018.
In 2018, more than two-thirds of the dry natural gas consumed in the United States was used by the electric power and industrial sectors. Smaller amounts of natural gas were consumed by the residential, commercial and transportation sectors; exported to other countries; or added to storage.
The U.S. electric power sector has been the largest end user of natural gas in three of the last four years, surpassing the industrial sector for the first time in 2012. About 35% of the natural gas consumed in the United States was used by the electric power sector to generate electricity and heat.
The industrial sector consumed 34% of natural gas in 2018 for process heating; as fuel for combined heat and power plants; and as raw material (feedstock) to produce chemicals, fertilizer, and hydrogen. The residential and commercial sectors use natural gas mainly for heating. P&GJ





Comments